说明:
3、本文未涉及大量的如VIDIOC_S_FMT等命令字,也不涉及V4L2采集模型,一来网络上很多这种说明(原创的,转载的),本文不想偷窃他人的成果;二来诸君如果看V4L2手册、看源代码的话,会学得更多,——如果肯下心思的话。
1、驱动——UVC 在Linux中,除了SPCA和GSPCA这类经典的USB摄像头驱动外,还有一种,即Linux UVC,全称为Linux USB Video Class,从Class这个词可以看出,UVC是代码某一类的视频设备驱动,官网上的说法包括了webcams, digital camcorders, analog video converters, analog 以及 digital television tuners等等。从2.6.26版本开始,Linux UVC驱动就纳入到内核中,不需要手动下载。但是需要自己手动配置内核,才可使用UVC。http://blog.chinaunix.net/u1/58951/showart_2199263.html
2、采集——V4L2 在Linux下,视频数据的采集有两套API,分别为V4L和V4L2。是Video For Linux的两个版本。其实在Windows下也有一套API,名为Video For Windows,即VFW,具体怎么使用,我没研究过,不过,按Windows的习俗,应该不难。
本文所用的API为V4L2,虽然它的第一个版本也可以使用,但是为了表明笔者与时俱进的精神,决心使用第二个版本。这个版本无外就下面三点:
1、打开或关闭摄像头设备都是调用POSIX标准的open或close,很简单;
摄像头的信息保存于自定义的结构体video_info中。如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 struct video_info { int camfd; /**< camera file descriptor */ struct v4l2_capability cap; struct v4l2_format fmt; struct v4l2_requestbuffers rb; struct v4l2_buffer buf; enum v4l2_buf_type type; void* mem[NB_BUFFER]; /**< main buffers */ uint8* tmp_buffer; /**< for MJPEG */ uint8* frame_buffer; /**< one frame buffer here */ uint32 frame_size_in; uint32 format; /**< eg YUYV or MJPEG,etc. */ int width; int height; int is_streaming; /**< start capture */ int is_quit; #ifdef DEBUG enum v4l2_field field; uint32 bytes_per_line; uint32 size_image; enum v4l2_colorspace color_space; uint32 priv; #endif };
在开始采集数据前,需要先看一下摄像头的信息,下面三个函数完成的功能分别为得到摄像头的属性(capability),得到摄像头的格式(format),设置摄像头的格式。属性包括了驱动信息,总线信息,是否支持流捕获等等;格式包括了摄像头数据格式(如MJPEG、YUYV等等),图像的宽、高等等。
1 2 3 4 int v4l2_get_capability(struct video_info* vd_info); int v4l2_get_format(struct video_info* vd_info); int v4l2_set_foramt(struct video_info* vd_info, uint32 width, uint32 height,uint32 format);
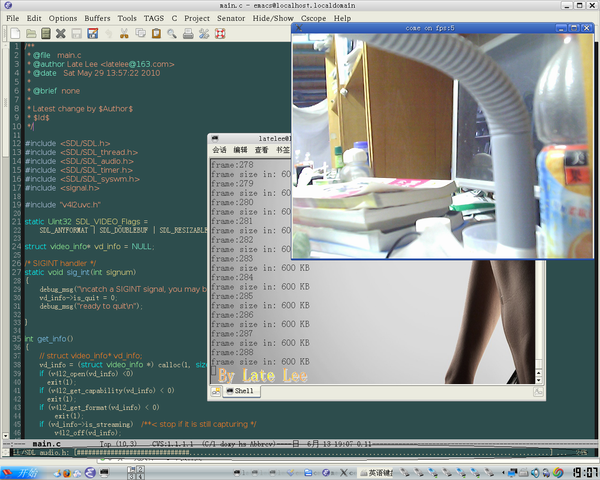
图1为在FC系统和ARM开发板上得到的摄像头信息。从图中可以清楚看到上述所讲的各种信息。至于最后一行的错误提示,是由于我调用v4l2_set_foramt将摄像头数据格式设置为YUYV出错了,即它不支持YUYV格式。然而,当我使用这个程序在红旗操作系统下测试时,结果又不同了,它是YUYV格式了!我将它设置为MJPEG格式,同样不行,所以图2最后同样出错。(那时正兴高采烈地做毕业设计,这个问题让我足足郁闷了好几天。我想不通是什么原因)
下面简单讲一下程序片段,具体的程序,参见附录中。
(1)、分配内存 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 switch (vd_info->format)/**< format will be also ok */ { case V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG: vd_info->tmp_buffer = (uint8 *)calloc(1, (size_t)vd_info->frame_size_in); if (vd_info->tmp_buffer == NULL) error_out("unable alloc tmp_buffer"); vd_info->frame_buffer = (uint8 *)calloc(1, (size_t)vd_info->width * (vd_info->height+8) * 2); if (vd_info->frame_buffer == NULL) error_out("unable alloc frame_buffer"); break; case V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV: vd_info->frame_buffer = (uint8 *)calloc(1,(size_t)vd_info->frame_size_in); if (vd_info->frame_buffer == NULL) error_out("unable alloc frame_buffer"); break; default: msg_out("error!n"); return -1; break; }
因为YUYV是一种原始数据,可以直接显示,不需要编解码,而MJPEG格式的,需要解码,所以分要分配两个缓冲区。
(2)、打开,O_NONBLOCK是以非阻塞方式打开。 1 2 3 vd_info->camfd = open(device, O_RDWR /*| O_NONBLOCK*/, 0); if (vd_info->camfd < 0) error_out("can not open the device");
(3)、查询 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &vd_info->cap)) error_out("query camera failed"); if (0 == (vd_info->cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE)) { debug_msg("video capture not supported.n"); return -1; }
(4)、设置格式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 memset(&vd_info->fmt, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_format)); vd_info->fmt.type= V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; vd_info->fmt.fmt.pix.width= width; vd_info->fmt.fmt.pix.height= height; vd_info->fmt.fmt.pix.field=V4L2_FIELD_ANY; vd_info->fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = format; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &vd_info->fmt)) error_out("unable to set format ");
(5)、查询缓冲区、映射到用户空间内存 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 memset(&vd_info->rb, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_requestbuffers)); vd_info->rb.count= NB_BUFFER; /**< 4 buffers */ vd_info->rb.type= V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; vd_info->rb.memory= V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &vd_info->rb)) error_out("unable to allocte buffers"); /* map the buffers(4 buffer) */ for (i = 0; i < NB_BUFFER; i++) { memset(&vd_info->buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer)); vd_info->buf.index= i; vd_info->buf.type= V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; vd_info->buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &vd_info->buf)) error_out("unable to query buffer"); /* map it, 0 means anywhere */ vd_info->mem[i] = mmap(0, vd_info->buf.length, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, vd_info->camfd, vd_info->buf.m.offset); /* MAP_FAILED = (void *)-1 */ if (MAP_FAILED == vd_info->mem[i]) error_out("unable to map buffer"); }
(6)、进入队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 /* queue the buffers */ for (i = 0; i < NB_BUFFER; i++) { memset(&vd_info->buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer)); vd_info->buf.index= i; vd_info->buf.type= V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; vd_info->buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &vd_info->buf)) error_out("unable to queue the buffers"); }
(7)、开始捕获(发出捕获信号) 1 2 3 4 5 6 vd_info->type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &vd_info->type)) error_out("unable to start capture"); vd_info->is_streaming = 1; debug_msg("stream on OK!!n"); debug_msg("===============================nn");
(8)、采集(从缓冲区队列中取出数据,再将数据的内存复制另一内存区) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 static int count = 0; if (!vd_info->is_streaming) /**< if stream is off, start it */ { if (v4l2_on(vd_info))/**< failed */ goto err; } memset(&vd_info->buf, 0, sizeof(struct v4l2_buffer)); vd_info->buf.type= V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; vd_info->buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; /* get data from buffers */ if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &vd_info->buf)) { msg_out("unable to dequeue buffern"); goto err; } switch (vd_info->format) { case V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG: if (vd_info->buf.bytesused <= HEADFRAME1) { msg_out("ignore empty frame...n"); return 0; } /* we can save tmp_buff to a jpg file,just write it! */ memcpy(vd_info->tmp_buffer, vd_info->mem[vd_info->buf.index], vd_info->buf.bytesused); /* here decode MJPEG,so we can dispaly it */ if (jpeg_decode(&vd_info->frame_buffer, vd_info->tmp_buffer, &vd_info->width, &vd_info->height) < 0 ) { msg_out("decode jpeg errorn"); goto err; } break; case V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV: if (vd_info->buf.bytesused > vd_info->frame_size_in) memcpy(vd_info->frame_buffer, vd_info->mem[vd_info->buf.index], (size_t)vd_info->frame_size_in); else memcpy(vd_info->frame_buffer, vd_info->mem[vd_info->buf.index], (size_t)vd_info->buf.bytesused); break; default: goto err; break; } /* here you can process the frame! */ v4l2_process(vd_info); /* queue buffer again */ if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &vd_info->buf)) { fprintf(stderr,"requeue errorn"); goto err; } debug_msg("frame:%dn", count++); debug_msg("frame size in: %d KBn", vd_info->frame_size_in>>10); return 0; err: vd_info->is_quit = 0; return -1;
(9)、停止捕获(发送停止信号) 1 2 3 4 5 6 vd_info->type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; if (-1 == ioctl(vd_info->camfd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &vd_info->type)) error_out("unable to stop capture"); vd_info->is_streaming = 0; debug_msg("stream off OK!n"); debug_msg("===============================nn");
(10)、关闭设备(释放内存、关闭设备) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 uint16 i = 0; if (vd_info->is_streaming)/**< stop if it is still capturing */ v4l2_off(vd_info); if (vd_info->frame_buffer) free(vd_info->frame_buffer); if (vd_info->tmp_buffer) free(vd_info->tmp_buffer); vd_info->frame_buffer = NULL; /* it is a good thing tounmap! */ for (i = 0; i < NB_BUFFER; i++) { if (-1 == munmap(vd_info->mem[i], vd_info->buf.length)) error_out("munmap"); } close(vd_info->camfd); debug_msg("close OK!n");
3、显示——SDL SDL是Simple DirectMedia Layer的简称,是一个自由的跨平台的多媒体开发包,适用于游戏、游戏SDK、演示软件、模拟器、MPEG播放器和其他应用软件。本文将它大材小用,用于显示采集得到的视频数据。
显示的代码片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 SDL_Surface *pscreen = NULL; SDL_Overlay *overlay = NULL; SDL_Rect drect; SDL_Event sdlevent; SDL_mutex *affmutex = NULL; unsigned char frmrate; unsigned char *p = NULL; uint32 currtime; uint32 lasttime; char* status = NULL; /************* Test SDL capabilities ************/ /* memory leak here */ if (SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't initialize SDL: %sn", SDL_GetError()); exit(1); } /* it need to alloc space! */ vd_info = (struct video_info *) calloc(1, sizeof(struct video_info)); /* init the camera,you can change the last three params!!! */ if (v4l2_init(vd_info, V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV, 640, 480) < 0) return EXIT_FAILURE; pscreen = SDL_SetVideoMode(vd_info->width, vd_info->height, 0, SDL_VIDEO_Flags); overlay = SDL_CreateYUVOverlay(vd_info->width, vd_info->height, SDL_YUY2_OVERLAY, pscreen); /* here?? */ p = (unsigned char *) overlay->pixels[0]; drect.x = 0; drect.y = 0; drect.w = pscreen->w; drect.h = pscreen->h; lasttime = SDL_GetTicks(); affmutex = SDL_CreateMutex(); /* big loop */ while (vd_info->is_quit) { while (SDL_PollEvent(&sdlevent)) { if (sdlevent.type == SDL_QUIT) { vd_info->is_quit = 0; break; } } currtime = SDL_GetTicks(); if (currtime - lasttime > 0) { frmrate = 1000/(currtime - lasttime); } lasttime = currtime; if (v4l2_grab(vd_info) < 0) { printf("Error grabbing n"); break; } SDL_LockYUVOverlay(overlay); /* frame_buffer to p */ memcpy(p, vd_info->frame_buffer, vd_info->width * (vd_info->height) * 2); SDL_UnlockYUVOverlay(overlay); SDL_DisplayYUVOverlay(overlay, &drect); /* dispaly it */ status = (char *)calloc(1, 20*sizeof(char)); sprintf(status, "come on fps:%d",frmrate); SDL_WM_SetCaption(status, NULL); SDL_Delay(10); } SDL_DestroyMutex(affmutex); SDL_FreeYUVOverlay(overlay); v4l2_close(vd_info); free(status); free(vd_info); printf("Clean Up done Quit n"); SDL_Quit(); return 0;
在红旗操作系统下测试如图3所示。最上面的即为SDL绘制的窗口(至于它向下调用什么图形库就不用理会了),中间的为控制台,它不断输出采集到的帧数以及每一帧的大小。最下面的是emacs。
为了演示emacs的多窗口gdb调试,现附上几个图。算是emacs篇的补充吧。
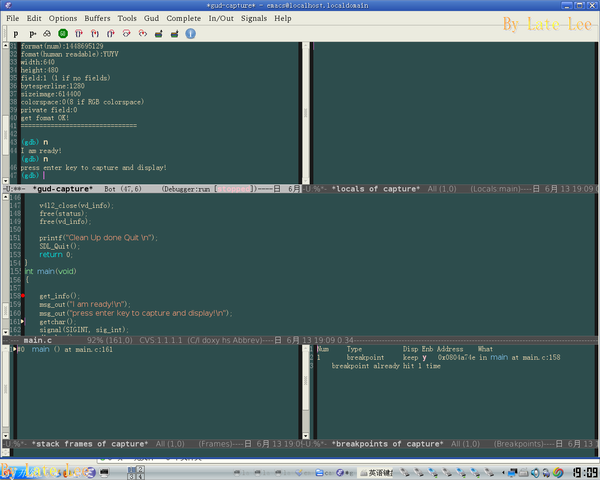
附图1中,已经加载了可执行文件,并设置了断点(命令为b main emacs,单步后,中间窗口出现红点即为断点处)。
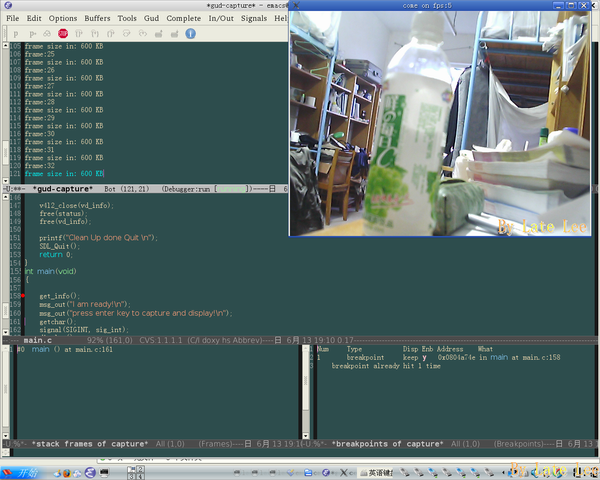
附图2所示的是正在显示图像,左上角即为控制台,出现的信息同上述截图一样。
附图3为结束的情形。重新回到gdb等待命令状态。
此时的emacs五个窗口中各有自己的功能,从上而下,分别为控制台、变量、源代码、帧栈以及断点。
看到了吧?emacs中调试不比VC差吧?
再附: UVC官网:http://www.ideasonboard.org/uvc/
V4L2官网:http://linux.bytesex.org/v4l2/
本文的程序下载:camera-pc-latelee.org.tar.bz2
luvcview项目下载:luvcview-20070512.tar.bz2
V4L2手册地址:http://v4l2spec.bytesex.org/v4l2spec/v4l2.pdf